How to protect the skin's hydrolipidic barrier?

Skin is, as you know, the largest part of our body. It is an organ that is connected to the inside of the body and what is outside it. Its main task is to protect internal organs. This is possible thanks to its specific, multi-layer structure. Among the layers of the skin, we should first of all mention the subcutaneous tissue, the dermis and, of course, the most familiar and visible to the naked eye, the epidermis, which protects the deep layers of the skin from penetration into microelements and pathogenic microorganisms unfavorable for the body, such as fungi, viruses, bacteria.
The task of the epidermis is also to prevent the loss of water from our body. If your epidermis is irritated, your skin feels tense, feels overly tight and sensitive, your skin's hydrolipidic barrier has likely been damaged.
Hydrolipid barrier - what is it?
The hydrolipid barrier is a protective layer of the skin consisting of water and lipids. The proportions in which these ingredients occur are not constant and change throughout the later years of our lives. Their ratio is also determined by the different types of skin pathologies that we may be dealing with. The protective layer of the epidermis consists of free fatty acids, epidermal lipids, structural proteins (eg collagen, filaggrin, elastin), squalene and NMF (natural moisturizing factor).
It is the well-balanced composition of these ingredients that protects us from the dangers to which we expose our skin every day. A strong lipid shell guarantees the skin an adequate level of hydration and nutrition and helps maintain its moisture. A good lipid layer is also the key to a youthful appearance. Thanks to it, the skin becomes elastic.
Damaged hydrolipidic barrier - how did this happen?
To cure the problem, and in this case restore the damaged lipid layer of our skin, it is necessary to discover the cause of the problem. Usually two elements contribute to its destruction. Firstly, there are unfavorable external factors that we do not fully influence, and secondly, inadequate, very aggressive skin care. Loss of lipids and finally destruction of the lipid layer is caused by, for example:
- Washing your face with hand soap, which is very drying.
- Rubbing the face vigorously with a rough towel.
- Too frequent and very aggressive peeling of the facial skin. Of course, regular exfoliation is important, but you shouldn’t overdo it. Exfoliating the epidermis every day, instead of helping it, will damage it. Exfoliate once or twice a week. On other days, focus on hydrating and repairing your skin.
- Excessive skin exposure to sun or frost. The weather also affects the condition of our skin, which is why it is so important to use highly nourishing creams in winter that protect the face from frost and cosmetics with sun protection. Remember that sunscreen for your skin is important all year round and should not be forgotten when the first cloudy autumn days arrive.
Restoration of the hydrolipid barrier
If your skin's protective coating has been compromised, don't worry—you can restore it. The key to success is properly selected care. It is worth including ingredients such as:
ceramides, which are also called intercellular cement. They are a natural ingredient that protects the skin from excessive water loss. Supplementing skin care with ceramides helps restore skin health.
Lactic acid in low concentration. This component is an acid from the AHA group. Regulates exfoliation and stimulates skin to naturally produce ceramides. It is worth keeping in mind not to use it in too high a concentration if you have a problem with a damaged protective layer of the epidermis. In low concentrations, this acid has moisturizing properties, and in high concentrations it has exfoliating properties.
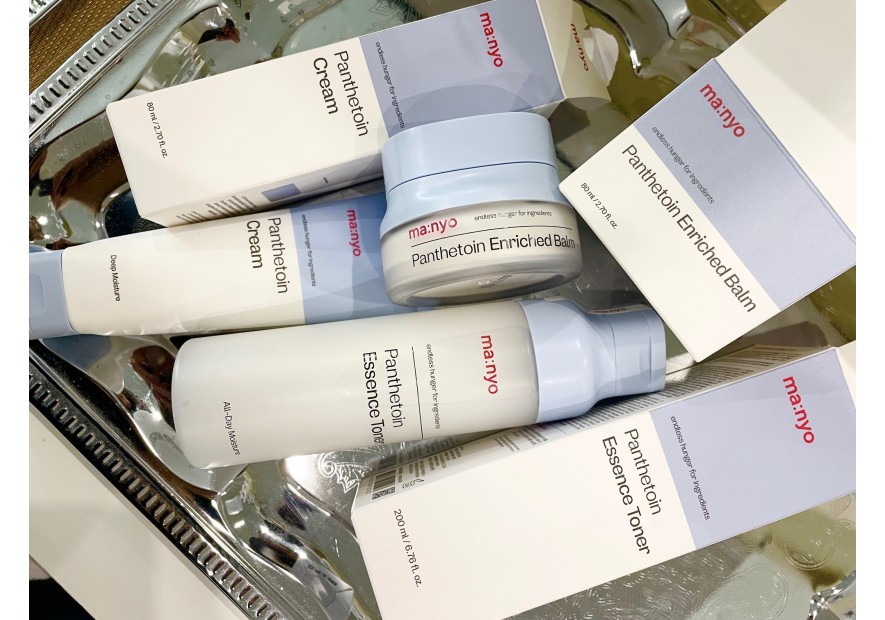
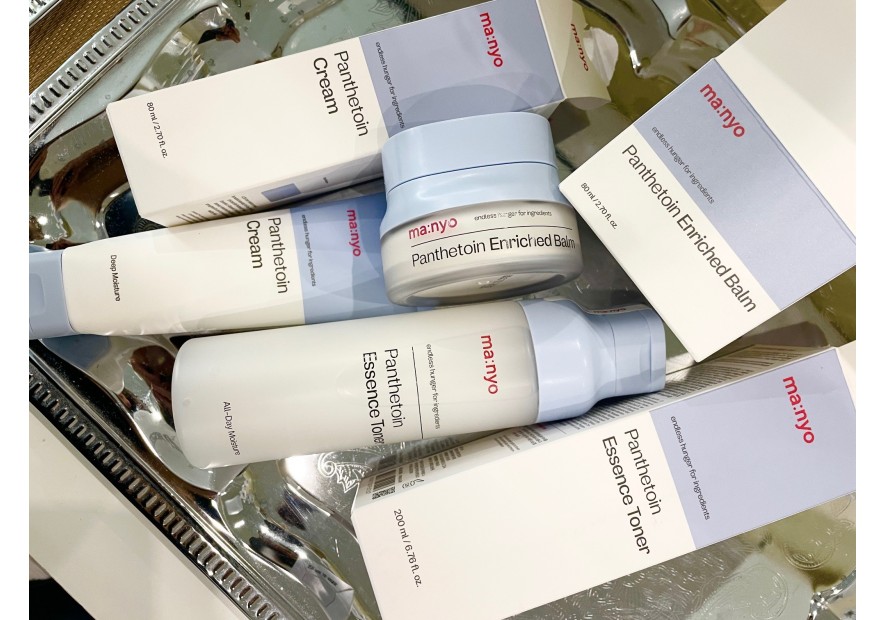
Panthenol to restore the skin's hydrolipid barrier
One of the most effective components for restoring the skin's protective barrier is panthenol.
Panthenol is a derivative of vitamin B5. D-Panthenol, also called provitamin B5, has the same biological activity as pantothenic acid.
Pantothenic acid has a stimulating effect on cell division; it is necessary for the proper metabolism of sugars, proteins and fats, as well as for the synthesis of certain hormones. It also accelerates wound healing, participates in tissue regeneration, improves pigmentation and hair condition, and is involved in the production of fats, cholesterol and neurotransmitters. A deficiency of this vitamin manifests itself in pathological changes such as excessive peeling or keratinization of the epidermis, pigmentation disorders or hair loss.
Panthenol plays an important role in maintaining proper skin condition. Has good healing and moisturizing properties. This is a powerful stimulator of cell renewal and growth of both the epidermis and dermis. Has a soothing effect on itching and redness.
Panthenol also has a very good moisturizing effect, which, combined with its penetrating abilities, makes it comparable to a natural moisturizing factor.
Panthenol not only retains water in the layers of the epidermis, but is also able to absorb it from the immediate environment. In addition, creams containing this ingredient have been shown to inhibit transepidermal water loss from the epidermis and at the same time lead to an increase in the skin's protective barrier. Panthenol has the ability to attract and retain water, so it moisturizes well and reduces dry skin. At the same time, unlike fats, it does not give the feeling of excessive lubrication. The use of preparations with this ingredient makes the skin smooth and soft, and has a calming effect on irritations. Dexpanthenol enhances the regeneration of dry and damaged skin. It penetrates very well into the deep layers of the skin, where it also has a soothing and anti-inflammatory effect. D-panthenol also has a protective effect and prevents irritations that can leave permanent damage and microscars on the skin.















































































Leave a comment